KFF research has consistently found prescription drug costs to be an important health policy area of public interest and public concern. Below are some key findings on the public’s experience with and perceptions of prescription drugs and their prices. For public awareness of some of the prescription drug cost provisions included in the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act, please see KFF’s July 2023 Health Tracking Poll.
About six in ten adults say they are currently taking at least one prescription drug and a quarter say they currently take four or more prescription medications.
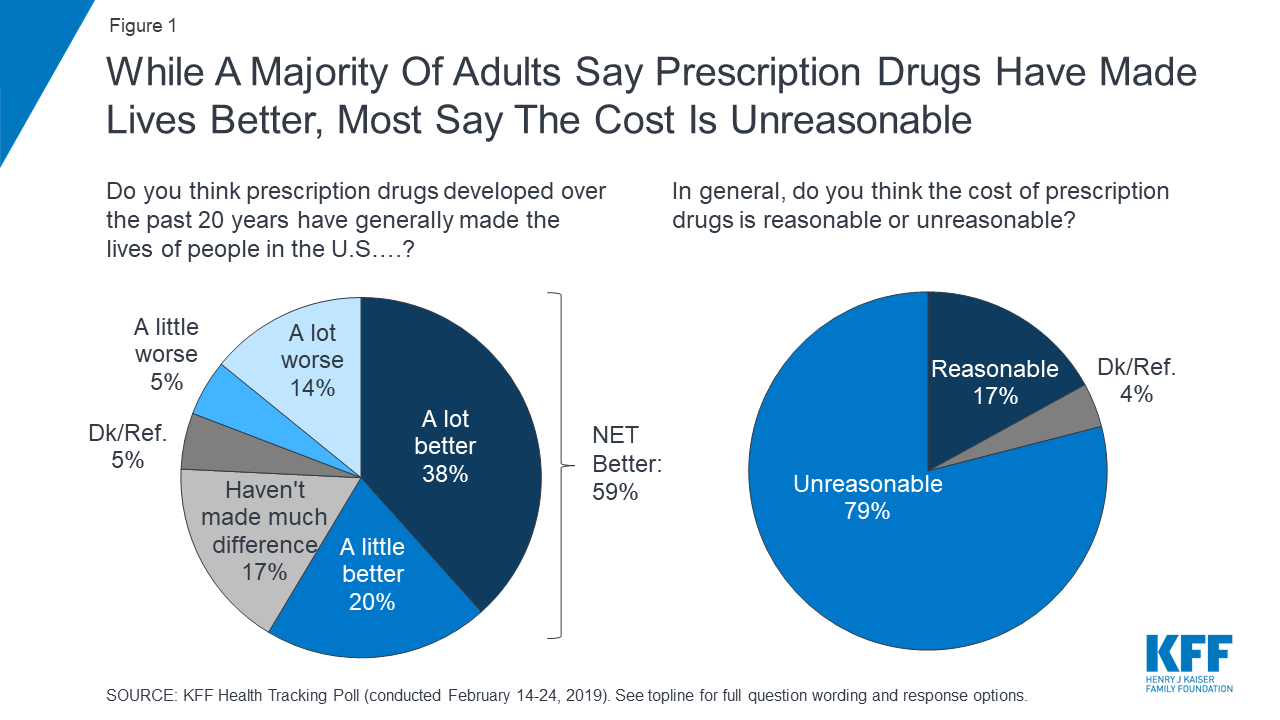
While about eight in ten adults (82%) say the cost of prescription drugs is unreasonable, most say affording prescriptions is either “very” or “somewhat easy” (65%).
Affordability is a bigger issue for those who are currently taking four or more prescription medicines. Nearly four in ten of those taking four or more prescription drugs say they have difficulty affording their prescriptions (37%), compared to one in five adults who currently take three or fewer prescription medications (18%). Individuals with annual household income of less than $40,000 are also more likely than adults with higher incomes to report difficulty affording their prescription medications.
About three in ten adults report not taking their medicines as prescribed at some point in the past year because of the cost. This includes about one in five (21%) who report that they have not filled a prescription or took an over-the-counter drug instead (21%), and 12% who say they have cut pills in half or skipped a dose because of the cost.
The share who report not filling a prescription, taking an over-the-counter drug instead, or cutting pills in half or skipping doses increases to four in ten among adult ages 18-29 (40%), Hispanic adults (39%), those taking four or more prescription drugs (37%), and those living in households with an annual income of less than $40,000 annually (37%).
The public sees profits made by pharmaceutical companies as the largest factor contributing to the price of prescription drugs. At least eight in ten across partisans say profits made by pharmaceutical companies are a “major factor” in the price of prescription drugs. This is followed by more than half who say the cost of research and development is a “major factor” contributing to the price, and about half saying that the cost of marketing and advertising is a major contributing factor to the cost of prescription drugs.
The July 2023 KFF Tracking Poll finds three in four adults saying there is “not as much regulation as there should be” when it comes to limiting the price of prescription drugs. Majorities across partisans, including eight in ten Democrats (82%), and about two-thirds of Republicans (68%) and independents (67%) say there is “not as much regulation as there should be” when it comes to limiting the price of prescription drugs.
Previous KFF polling finds that when it comes to lowering the cost of prescription drugs, majorities of partisans trust their own party to do a better job on this issue. Independents are more likely to trust the Democratic Party than the Republican Party to do a better job of lowering the price of prescription drugs.
Despite this, neither party in Congress has gained the full confidence of the public to do what’s right for the country on prescription drug pricing. Slightly less than half of the public say they have “a great deal” or “a fair amount” of confidence in President Biden (46%) or Democrats in Congress (48%) to recommend the right thing for the country on prescription drug prices. One-third of the public (33%) say they have at least a fair amount of confidence in Republicans in Congress and few are confident that pharmaceutical companies will recommend the right thing (14%).
Half of adults are confident in AARP’s ability to recommend the right thing for the country on prescription drug pricing. AARP is a non-partisan interest group focusing on the issues that impact adults over the age of 50 that has strongly advocated for Medicare drug negotiations.
KFF has been asking about various proposals aimed at lowering the cost of prescription drugs for decades including many addressed in the Inflation Reduction Act which was passed in 2022. Majorities, across partisans, support a wide range of proposals including most notably – allowing the federal government to negotiate with drug companies to get a lower price on medications. Majorities also favor increasing taxes on drug companies that refuse to negotiate the price of their drugs with the government, limiting how much drug companies can increase the price of drugs based on annual inflation rates, allowing Americans to buy drugs imported from Canada, placing an annual limit on out-of-pocket drug costs for people with Medicare, and making it easier for generic drugs to come to market.
Support for these policies does range slightly among partisans and after hearing arguments in favor or against each proposal.
Nonetheless, despite concerns about costs, the public generally sees the benefits of prescription medicines as more than six in ten adults believe prescription drugs developed over the past 20 years have generally made the lives of people in the U.S. better.


