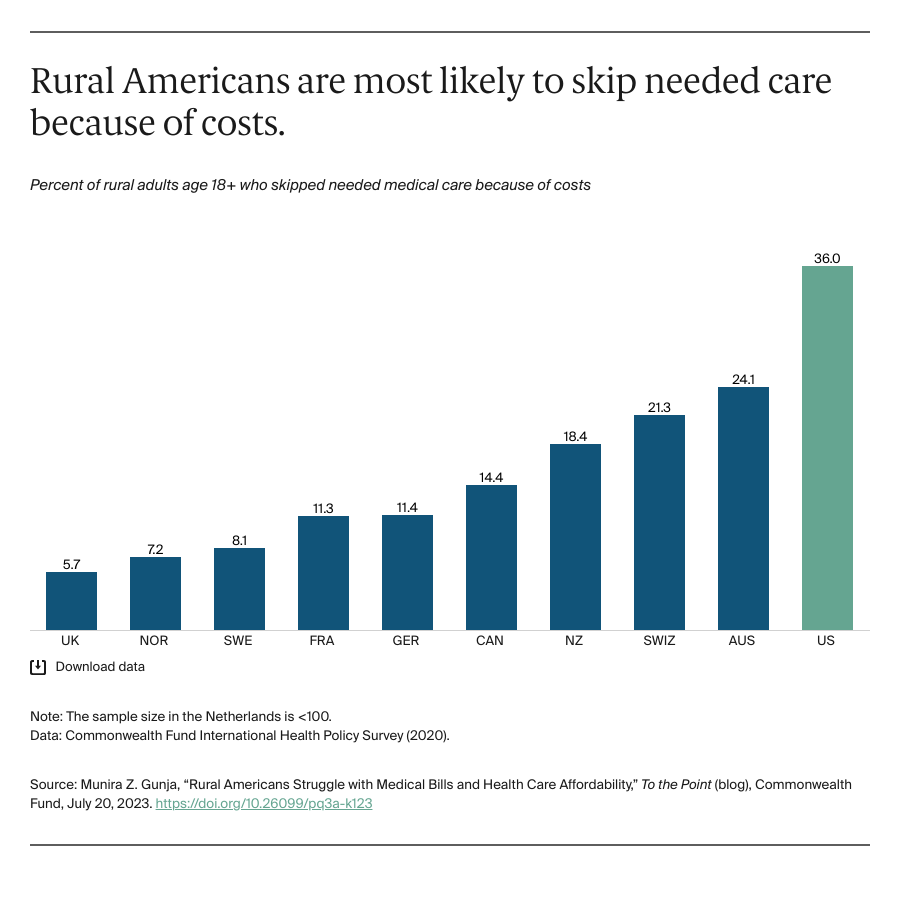
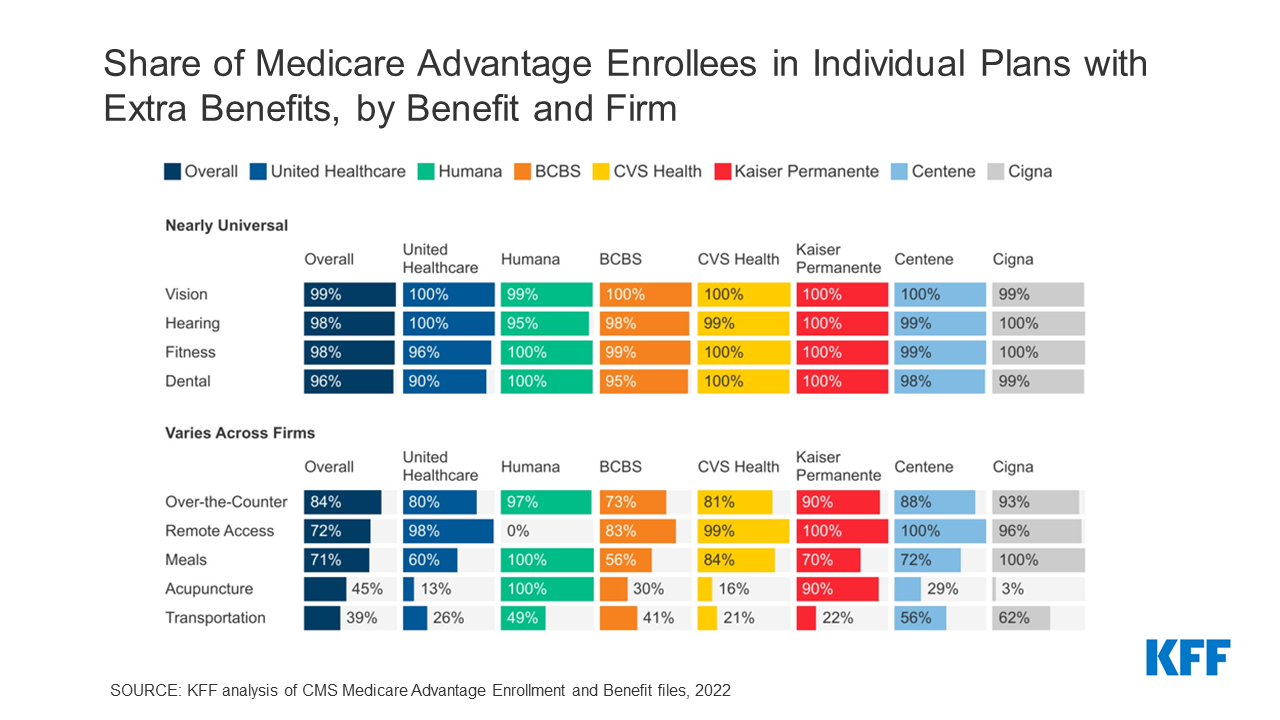
Lobbying groups representing different camps of the healthcare industry have come together to urge the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Service (CMS) to reconsider “conflicting regulatory proposals” that require different electronic standards for electronic data exchanges during prior authorization.
Lobbying groups representing different camps of the healthcare industry have come together to urge the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Service (CMS) to reconsider “conflicting regulatory proposals” that require different electronic standards for electronic data exchanges during prior authorization.
The American Hospital Association, the American Medical Association and the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association’s joint letter to CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure addresses proposed rule-making released by the agency in December 2022.
It will require payers and states to streamline prior authorization processes and improve the electronic exchange of health data by 2026, including through the use of a Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) application programming interface (API) able to handle electronic prior authorization. The proposed rule also contains incentives for hospitals and physicians to adopt electronic prior authorization.
The provider and payer groups told the administrator that, while they appreciate the push to reduce administrative burden and reform prior authorization, the administration must not move forward with the proposed current prior authorization standards provisions that “create the very same costly burdens that administrative simplification seeks to alleviate.”
One proposed rule regarding electronic prior authorization information exchange (CMS-0057-P) requires federally regulated health plans to offer Health Level 7 (HL7) FHIR-based APIs, while another (the prior authorization attachment standards provisions) requires all health plans under the HIPAA regulatory pathway to use a combination of HL7 standards and the X12 standard.
“We are concerned by the conflicting provisions of these NPRMs that would establish two different sets of standards and corresponding workflows to complete the PA process, depending on the type of health plan,” the groups wrote. “Moreover, for federally regulated plans, this would require cross-walking the two standards for no discernable benefit.”
The end result, they wrote, would be “widespread industry confusion” and major expenses for plans and providers needing to implement the conflicting technologies to meet the proposed rules’ requirements.
“For these reasons, our organizations strongly advise against adoption of standards for PA attachments as proposed in this rule,” they wrote.
Hundreds of federal legislators from both sides of the aisle have pushed CMS to more quickly finalize its proposed updates to prior authorization, which, in its current form, lawmakers and other critics have characterized as a costly and overwrought administrative burden. They also called for the agency to go further and shorten delays by shortening the window for a response to an expedited prior authorization request and to include a mechanism enabling real-time decisions for routine approvals.